File Transfer Protocol
Anyone who wants to quickly and easily transfer a relatively large amount of data over a network connection today typically uses the File Transfer Protocol, or FTP. This is a client-server-based network protocol that allows data to be transferred in a TCP-IP network. It is one of the oldest protocols, having existed since 1971. It is used in IT security.
Data transfer – both uploading and downloading – is done through an appropriate access, which can be executed by any client via a simple command line. Usually, one of the common web browsers is sufficient to work with File Transfer Protocol. This means, in theory, you can access an FTP server containing the relevant data from any computer.
For all users who need a graphical interface to handle File Transfer Protocol, there are various programs available that can be installed on a computer or laptop. Typically, these FTP programs are very similar to the folder system of well-known computer systems like Windows or Linux, making them intuitive to use. There is also freeware that has proven itself for several years.
Technical process of the File Transfer Protocol
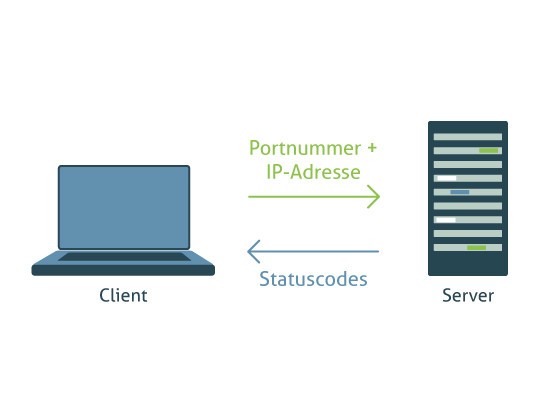
If you want to transfer data using the File Transfer Protocol, a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection is first established from the FTP client to the server via a control channel. On the server side, port 21 is used for this. Subsequently, the connection is established in a second step via port 20. The client and server exchange data over the data connection.
At the beginning of the connection with an FTP server, the user must authenticate with a username and password. Subsequently, the user can select the respective files on the server and download them to their computer. Alternatively, it is also possible to upload data from a computer to the server. Each process is independent, so a new TCP connection must be established with each new "contact." The TCP protocol handles error control during data transmission. There are specific commands for sending, retrieving, renaming, and deleting files, as well as for setting up, deleting, and switching directories.
Development and current usage of FTP
Already at the beginnings of the internet, or rather its predecessor, the ARPANet (military network), the File Transfer Protocol was developed. Even back then, it served to make data available or to facilitate the exchange of documents and information as easily as possible. Likewise, there was no need to resort to other (external) services like an email provider, especially when it involved sensitive information.
Nowadays, the File Transfer Protocol is used in almost all areas of business and research: from universities or colleges that provide software and information through public access to marketing agencies that want to conduct larger data exchanges with their clients. In this context, it is worth mentioning that data exchange via File Transfer Protocol can also be encrypted. With encryption – for example, through Transport Layer Security – the client must authenticate with the host. For this, the user receives a username and password, which allows access to the FTP server and the ability to conduct data exchange or transfer. This is especially advisable when important company data needs to be exchanged.
A special feature of the File Transfer Protocol is the anonymous mode. This allows you to log in anonymously and download data. Modifying files or a directory is usually not permitted for the anonymous visitor.
By the way, an FTP server is not only accessible in a web browser, but almost every operating system also has an accessible File Transfer Protocol server.